Living
Marine Fungus Shows Promise in Tackling Ocean Plastic Pollution
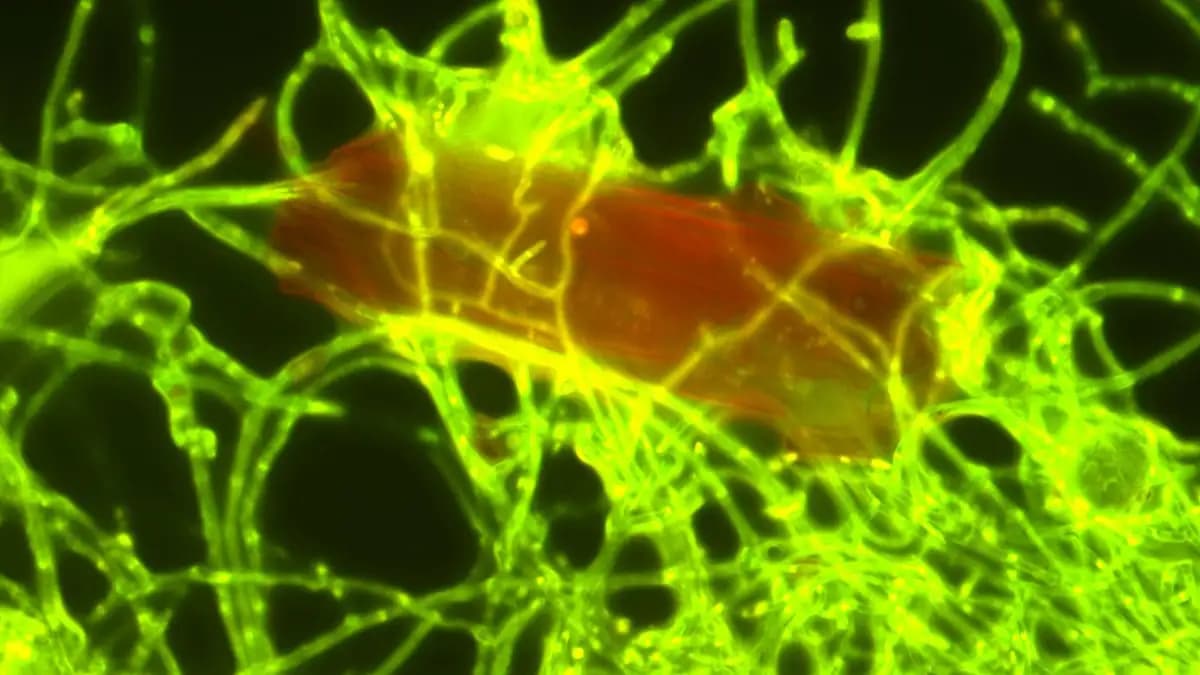
In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have identified a marine fungus with the ability to break down polyethylene, a common plastic, when exposed to UV light. This revelation opens up new possibilities in the fight against ocean plastic pollution.
The marine fungus, Parengyodontium album, was found to degrade polyethylene after exposure to UV radiation, suggesting the presence of other plastic-degrading fungi in deeper ocean waters. Researchers, including those from the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ), have shown that this fungus can break down plastic particles, adding to the limited list of known plastic-degrading marine fungi, which previously included only four species.
Parengyodontium album resides in thin layers on plastic debris, living alongside other marine microbes. The research, published in the journal Science of the Total Environment, involved scientists from NIOZ, Utrecht University, the Ocean Cleanup Foundation, and various European research institutes. Their findings indicate that the fungus decomposes polyethylene (PE), the most prevalent plastic in the ocean, converting it primarily into carbon dioxide.
To accurately monitor the degradation process, researchers collected plastic debris from pollution hotspots in the North Pacific Ocean and isolated the fungus in a laboratory setting. They used specially labeled carbon isotopes to trace the carbon flow within the degradation products. “These so-called 13C isotopes remain traceable in the food chain. It is like a tag that enables us to follow where the carbon goes. We can then trace it in the degradation products,” explained lead author Annika Vaksmaa.
Vaksmaa expressed excitement over the quantifiable nature of this research, noting that the breakdown of PE by P. album occurs at a rate of approximately 0.05 percent per day. Interestingly, the fungus utilizes only a small fraction of the carbon from PE, excreting most of it as carbon dioxide. While CO2 is a greenhouse gas, the amount released by the fungus is comparable to what humans emit through respiration.
The study highlights the critical role of UV light in enabling the fungus to use PE as an energy source. “In the lab, P. album only breaks down PE that has been exposed to UV-light at least for a short period of time. That means that in the ocean, the fungus can only degrade plastic that has been floating near the surface initially,” Vaksmaa noted. This finding underscores the dual role of UV light in both mechanically and biologically breaking down plastic in marine environments.
Despite the promising potential of P. album, it is limited to degrading plastics near the ocean’s surface. Vaksmaa and her team believe other, yet-to-be-discovered fungi could be breaking down plastics in deeper waters. “Marine fungi can break down complex materials made of carbon. There are numerous amounts of marine fungi, so it is likely that in addition to the four species identified so far, other species also contribute to plastic degradation. There are still many questions about the dynamics of how plastic degradation takes place in deeper layers,” she said.
The urgency of finding plastic-degrading organisms cannot be overstated, given the staggering amounts of plastic produced annually—over 400 billion kilograms, with projections to triple by 2060. Much of this plastic ends up in the ocean, accumulating in subtropical gyres, where ring-shaped currents trap debris. The North Pacific Subtropical Gyre alone has collected approximately 80 million kilograms of floating plastic, illustrating the scale of the challenge.
Lead author Vaksmaa emphasized the significance of their discovery, noting the critical need for further research to uncover more plastic-degrading fungi and better understand the mechanisms of plastic breakdown in the ocean’s depths.
Living
Texas Mom Welcomes Third Baby at 51 — and Says She Might Not Be Done Yet
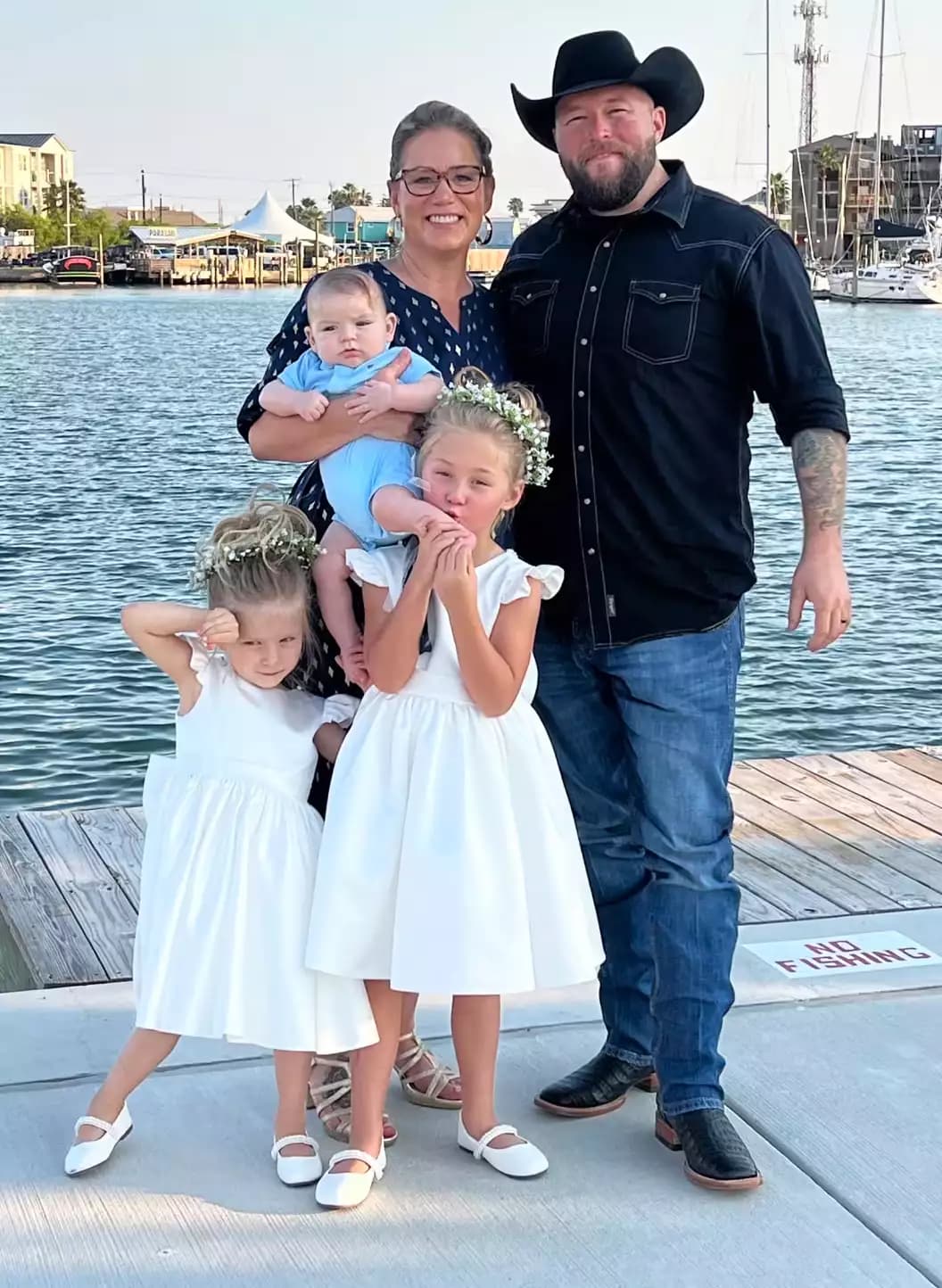

Grace Collins, a mom from Texas, isn’t letting age define her motherhood journey. At 51, she recently welcomed her third child — a baby boy named A.J. — and says she’s not sure she’s finished growing her family just yet.
Collins first gained attention in 2024 when she went viral on TikTok for sharing her story of becoming a mom later in life through IVF. Her journey began at age 44 with the birth of her first daughter, Maggie. Two years later came her second daughter, Goldie. And in 2024, at age 50, she became pregnant again — this time with her first son.
“It’s hard being pregnant no matter what age you’re at,” Collins told TODAY.com. “And I don’t know if I’m done either!”
Though being pregnant in her 50s might seem daunting, Collins says it’s actually gotten easier over time. “I felt like I was more tired when I was pregnant at 44 than I was when I was 50,” she previously told PEOPLE. “Maybe my body just figured out how to cope, or maybe having children keeps me young.”
That sense of energy seems to carry into her everyday life as a mom of three little ones. “I’m a pretty on-the-go kind of girl,” she said. “I’ve been in the little kid daily grind since I was 44, so I don’t know any different.”
Collins also shared that age has brought some unexpected advantages. With more life experience under her belt, she feels more aware of her body and committed to her health. Before her last pregnancy, she took proactive steps to ensure she was in good shape, including a full slate of medical screenings and maintaining an active lifestyle.
“I made sure I had a healthy baseline,” she told PEOPLE. “All my pregnancies have had their hurdles — but overall, I can honestly say it’s become easier with each one.”
Despite being older than many of the parents she meets at playdates or school events, Collins says age isn’t a barrier when it comes to connecting. “The things we have in common outweigh our age differences,” she said. “If anything, having kids has honestly kept me younger.”
As for whether baby A.J. will be her last? Collins isn’t closing that door just yet. For now, she’s savoring life as a busy mom and embracing every moment. “I’m going to do everything I can to stay young and present — not just for my kids but for myself.”
Living
Friendship Benches Come to Sussex, Offering Free Mental Health Support Inspired by Zimbabwe
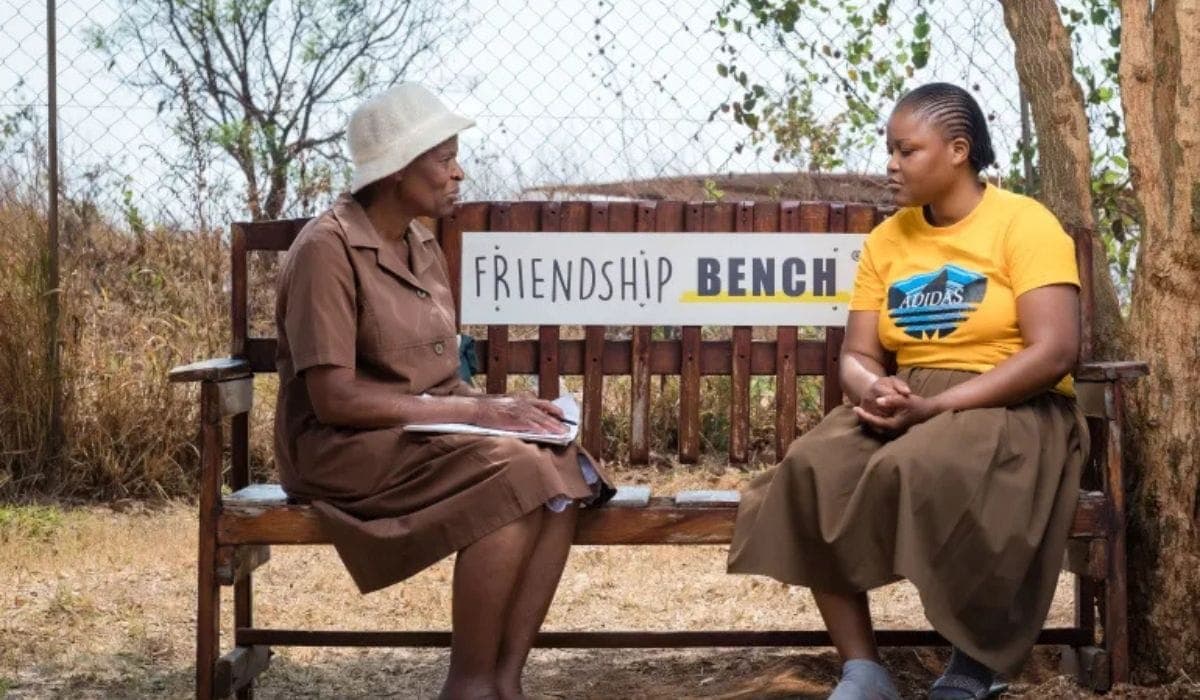

A simple wooden bench may seem unremarkable, but in Sussex, it’s about to become a powerful tool for tackling mental health challenges.
A pilot scheme called the Friendship Bench, originally developed in Zimbabwe, is launching in Sussex to provide free, low-barrier support for people dealing with depression, anxiety, and loneliness. The initiative places trained lay counsellors—affectionately called “grandmothers” and “grandfathers”—on benches in public indoor spaces like libraries and community centers, where they offer compassionate, non-judgmental conversation to anyone who stops by.
Founded in 2006 by psychiatrist Professor Dixon Chibanda, the Friendship Bench model was born from the idea that everyday people, especially older members of the community, can offer meaningful support. Despite receiving just two weeks of training, the lay counsellors have made a global impact. Studies, including one published in The Journal of the American Medical Association, show the program led to an 80% reduction in depression and suicidal thoughts, and a 60% improvement in quality of life among participants.
Now brought to the UK by Dr. Nina Lockwood of Brighton and Sussex Medical School, the Sussex pilot will involve ten lay mental-health workers offering six-to-eight-week support sessions. Unlike the original Zimbabwe benches that are placed outdoors, the UK’s version will adapt to the British climate with indoor seating areas.
“There is an unintended novelty to the west taking a model founded in Africa,” Lockwood said. “But just like in Zimbabwe, the UK has a massive shortfall in mental health resources compared to the demand of our population’s mental health problems. We urgently need to adopt agile, alternative ways of working.”
Trained volunteer Mebrak Ghebreweldi, from Diversity Resource International, said the approach allows time to uncover root issues, like housing insecurity or unemployment—problems that can be missed in rushed GP visits.
“GPs don’t have time for those long conversations,” Ghebreweldi explained. “They’ll just prescribe something. But when we listen, we often find that what seems like depression may actually stem from practical, solvable problems.”
Chibanda’s vision for the Friendship Bench grew from a recognition that medication and diagnoses alone can’t fix a growing global mental health crisis. “Not everyone can see a mental health professional,” he said. “But most people have access to the care, compassion, and wisdom of grandmothers—the unsung heroines of the world.”
In the UK, mental health needs are urgent. One in six adults reported moderate to severe depressive symptoms in 2022, and NHS wait times for therapy can stretch over four months. The Friendship Bench offers a hopeful alternative—one built on human connection and community.
With over half a million people already helped worldwide, the scheme’s expansion into Sussex could be a quiet revolution in how we approach mental wellness—one chat at a time.
Living
New Coral Feeding Device Offers Hope for Reef Restoration

A team of scientists from The Ohio State University has unveiled a groundbreaking device designed to enhance food sources for coral reefs, offering a potential boost to restoration efforts. The device, called the Underwater Zooplankton Enhancement Light Array (UZELA), works by attracting zooplankton to coral habitats, increasing their availability as a food source.
UZELA is a submersible, programmable light capable of operating for up to six months on a single battery. When maintenance is needed, trained divers can perform simple servicing. The device activates for roughly an hour each night, emitting a specific type of light that encourages zooplankton accumulation without disturbing other marine species. This process enhances the feeding opportunities for corals, improving their chances of survival and growth.
Encouraging Results from Initial Tests
Researchers tested UZELA near two native Hawaiian coral species, Montipora capitata and Porites compressa. Their observations showed a seven-fold increase in local zooplankton populations and a dramatic improvement in coral feeding rates—ranging from 10 to 50 times higher than usual. These findings were published in Limnology and Oceanography: Methods.
According to study lead Andréa Grottoli, a professor of earth sciences at The Ohio State University, coral reefs play a disproportionately important role in marine ecosystems. “Although reefs make up less than 1% of the ocean, they support a third of all marine life,” she explained. “With increasing threats, we must find ways to protect them.”
The Growing Threat of Coral Bleaching
Extreme ocean temperatures continue to endanger coral reefs. The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) recently reported that from February 2023 to April 2024, nearly 60.5% of the world’s coral experienced bleaching. This occurs when corals expel the algae that provide them with essential nutrients, making them more susceptible to disease and die-off.
While corals can recover if water conditions stabilize, many struggle due to a lack of available food. The presence of concentrated zooplankton, as facilitated by UZELA, could help mitigate some of the negative effects and provide corals with the nutrition they need to survive.
A Short-Term Solution with Long-Term Potential
Although UZELA is not a permanent fix for coral degradation, researchers see it as a valuable tool for temporary relief. Grottoli compared it to “a band-aid that could help buy us time” while broader solutions, like reducing carbon emissions, are pursued.
Currently, UZELA devices are assembled by hand, but researchers are working with a local engineering firm to refine the design for mass production. If successful, an improved version could be ready within the next few years, allowing for expanded deployment in vulnerable coral reef regions.
“Addressing climate change is the only way to truly save coral reefs,” Grottoli emphasized. “But tools like UZELA give us a fighting chance to protect some reefs while we work toward a more sustainable future.”
Living
Kazakhstan’s Snow Leopard Population Soars Toward Historic Highs
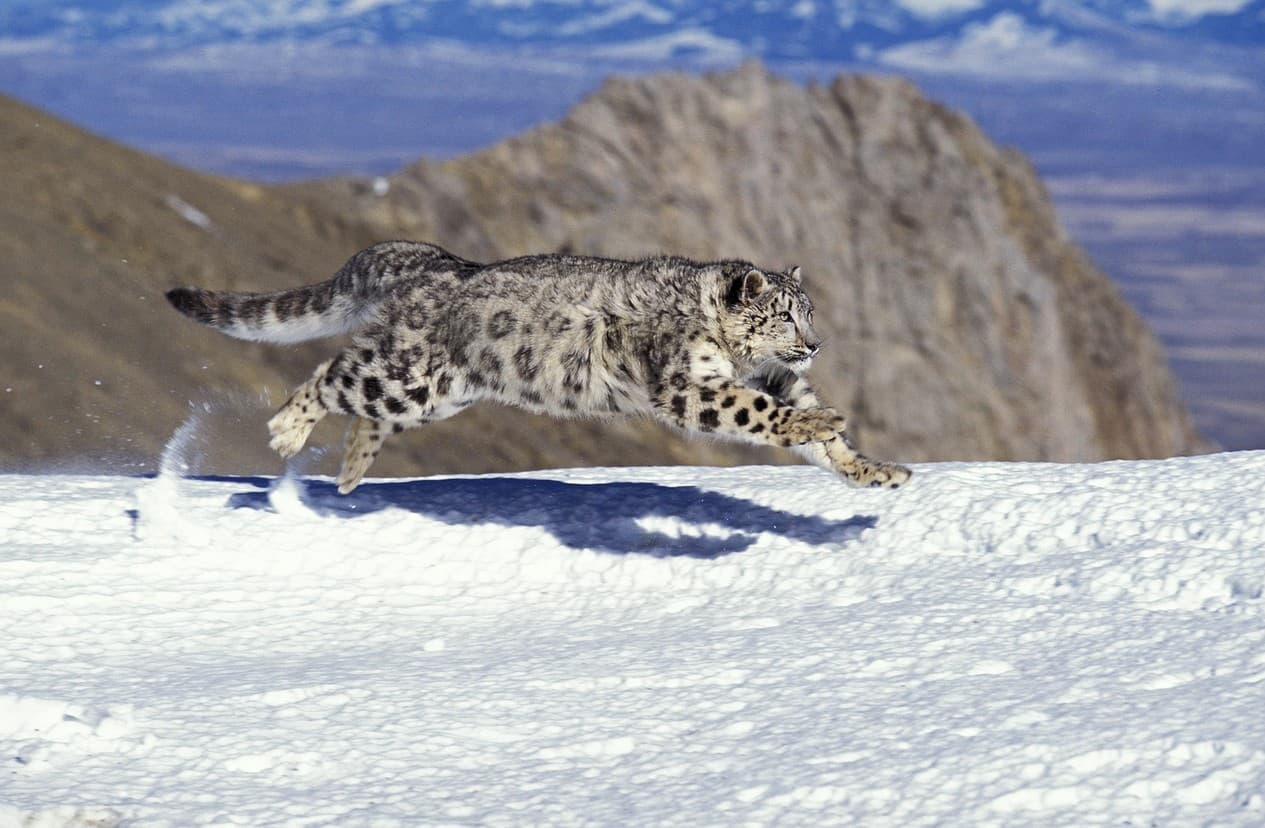

Kazakhstan’s snow leopard population has made a remarkable recovery, with current estimates ranging from 152 to 189 individuals. These numbers echo those last seen in the 1980s, marking a milestone in global conservation efforts. However, human activities continue to pose significant challenges to the survival of this elusive species.
Known locally as the irbis, the snow leopard is classified as vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s (IUCN) Red List. It is also listed in the national Red Books of all 12 countries within its range. In Kazakhstan, snow leopards inhabit rugged mountainous regions, including the Altai, Tien Shan, Zhetysu Alatau, and other large mountain systems.
Since 2018, Kazakhstan has implemented a snow leopard conservation initiative under the United Nations Development Program (UNDP). This effort has led to a population increase of over 26% since 2019. Alexei Grachev, executive director of the Snow Leopard Foundation and head of the Snow Leopard Monitoring Center, emphasized that protected areas have played a pivotal role in stabilizing and boosting the population.
Key habitats include Ile-Alatau National Park, Altyn-Emel National Park, and the Katon-Karagai Reserve. The Zhetysu region, in particular, has the highest population density due to favorable factors such as plentiful prey, effective protection measures, and minimal human interference. In contrast, the Katon-Karagai Reserve’s snow leopard population remains small but is showing signs of recovery. Photo traps first confirmed their presence in 2020, and a recent sighting of a female with two cubs offers hope for continued growth.
Ongoing Threats and Conservation Efforts
Despite the positive trends, snow leopards face persistent threats, including poaching, habitat disruption from expanding economic activities, climate change, and conflicts with local communities. To address these issues, Kazakhstan is working to expand protected areas, such as the proposed Merken Regional Park in Zhambyl Oblast. The use of satellite telemetry has also advanced conservation efforts, with 11 snow leopards collared in 2021 to monitor their movements and behaviors.
High mortality rates among young snow leopards remain a concern. Juveniles often migrate to neighboring countries where the risk of human-wildlife conflict is higher. To reduce such conflicts, Kazakhstan offers financial compensation to herders for livestock losses caused by snow leopards, aiming to prevent retaliatory killings.
International Recognition and Collaboration
Kazakhstan’s achievements in snow leopard conservation have drawn international acclaim. While many countries struggle with declining or stagnant snow leopard populations, Kazakhstan has demonstrated measurable progress. Collaborative efforts with Kyrgyzstan, supported by international agreements, have further strengthened regional conservation initiatives. UNDP projects have enhanced protection in 14 natural areas across Kazakhstan, utilizing advanced tools such as camera traps, drones, and thermal imaging devices.
The resurgence of Kazakhstan’s snow leopard population stands as a testament to effective and sustained conservation strategies. By safeguarding this iconic predator, the country contributes to global biodiversity and highlights the importance of proactive environmental stewardship.
Living
Study Highlights the Mental Health Benefits of Time Outdoors for Children
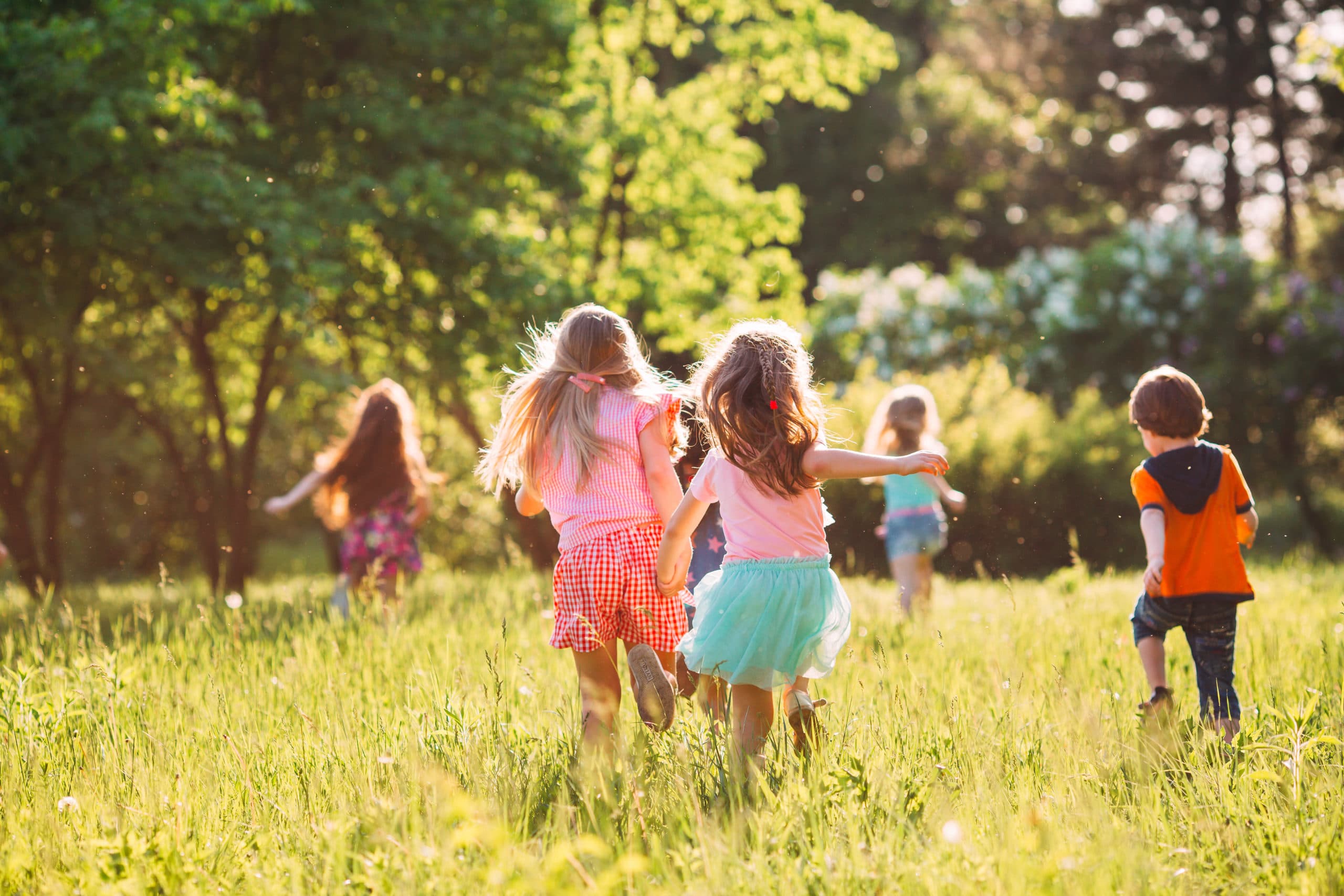

A new study has found that spending time in nature can significantly improve the mental health of children, particularly those with pre-existing emotional challenges. The research, published in JAMA Network Open, demonstrates that even simple, low-cost programs involving time outdoors can lead to remarkable benefits for children aged 10 to 12.
Nature as a Mental Health Equalizer
The study, conducted in Quebec, Canada, involved over 500 schoolchildren who participated in a three-month program in the spring of 2023. Researchers found that children with the most significant mental health issues—such as anxiety, depression, aggressiveness, and social difficulties—experienced the greatest improvements after spending two hours a week in natural environments.
Study senior author Professor Marie-Claude Geoffroy of McGill University highlighted the transformative effects:
“We found that children with higher mental health symptoms at baseline showed greater reductions in symptoms following the intervention.”
The intervention acted as a mental health equalizer, reducing disparities among children and offering particular support to those most vulnerable.
The Program: Learning in Nature
As part of the program, teachers moved regular class activities—such as lessons in math, science, and languages—into local parks or green spaces for two hours each week. Additionally, they included 10- to 15-minute activities aimed at promoting mental health. Examples included:
- Drawing a tree
- Writing haikus
- Mindful walking
The study’s first author, Tianna Loose from the University of Montreal, emphasized the simplicity and accessibility of the approach:
“The intervention was low-cost, well-received, and posed no risks, making it a promising strategy for schools with access to greenspaces.”
Positive Outcomes for Students and Teachers
At the end of the program, teachers reported that students were calmer, more relaxed, and more attentive in class after their outdoor sessions. The most significant behavioral improvements were observed in children who had exhibited high levels of distress at the start of the study.
The findings build on observational research and mark the first time a randomized controlled trial has been used to evaluate the mental health benefits of nature for children. The study aligns with a recent UNICEF report underscoring the importance of green spaces for childhood development.
Inspiration from the Pandemic
The project was inspired by the COVID-19 pandemic, when concerns arose about children spending excessive time indoors. Professor Geoffroy shared how her own experiences influenced the study:
“My kids and I spend lots of time in parks, so I’ve seen the benefits of spending time in nature, both for myself and for them. I thought, maybe we can create a free and accessible intervention for school children to experience similar benefits.”
Next Steps: Teenagers and Climate Anxiety
The research team plans to expand their work to include teenagers, co-designing nature-based programs aimed at reducing climate anxiety, improving well-being, and fostering a deeper connection to the environment.
Co-author Professor Sylvana Côté from the University of Montreal noted the broader implications of the findings:
“This suggests that nature-based programs may offer targeted benefits for children with higher levels of mental health vulnerabilities and potentially act as an equalizer of mental health among school-age children.”
A Simple Yet Powerful Solution
With schools increasingly recognizing the value of mental health support, this study highlights the potential of outdoor learning programs. By incorporating nature into the school day, educators can provide children with a calming, restorative environment that improves emotional well-being, focus, and social interaction—all without significant costs or risks.
As schools consider innovative ways to support students, nature-based interventions offer a promising solution that benefits both children and their communities.
-

 OMG7 years ago
OMG7 years agoA Couple Gave Birth to the Most Beautiful Twins Ever
-

 OMG7 years ago
OMG7 years ago20 Rare Historical Photos
-

 OMG7 years ago
OMG7 years agoHilarious Airport Photos
-

 Cute7 years ago
Cute7 years agoMom Refuses to Let Daughter Eat Sugar and Years Later This is What She Grows Into
-

 OMG6 years ago
OMG6 years agoTop Secret Air Force One Facts That You Never Knew
-
OMG6 years ago
The Funniest Yearbook Photos Of All Time
-

 OMG7 years ago
OMG7 years agoRetired Mathematician Restores Log Cabin
-

 OMG5 years ago
OMG5 years agoWhat Happened When This ‘Duck Dynasty’ Legend Chopped Off His Beard?